Ever wanted to read up on interesting developments in science and medicine but found the content too monotonous or difficult to comprehend?
These articles break down new studies into concise, easy-to-understand language.
These articles break down new studies into concise, easy-to-understand language.
Melatonin in Improving IBS Symptoms
Crystal Ma, March 31 2024
Irritable Bowel Syndrome, or IBS, is a chronic condition that is one of the most common gastrointestinal (GI) disorders, affecting up to 15% of the United States population. This condition is characterized by symptoms such as abdominal pain, frequent bowel movements, and changes in stool consistency, causing constant discomfort for individuals affected. As IBS is a disorder in which symptoms vary among individuals, and there is no cure at the moment, current treatments do not fully satisfy all patients’ demands. As a one-size-fits-all treatment remains elusive, there is importance in seeking additional supplements or treatments which can be utilized in conjunction.
Fishy Business: Omega-3s Might be your Mood and Heart's BuddyCharissa Mak, March 31 2024
In a world where the relentless grip of cardiovascular diseases (CVDs) and the weight of major depressive disorder (MDD) cast long shadows, a recent scientific exploration unveils a potential ray of hope for those navigating the intricate terrain where heart health meets mental well-being. Dive into the intriguing study that dares to ask: can omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids (n-3 PUFAs) be the game-changer for the somatic and fatigue symptoms affecting individuals facing the dual challenges of heart-related issues and depression?
The Neuroscience of Love and SeparationEleanor Gorham, March 31 2024
Does absence really make the heart grow fonder? In a recent study a group of researchers led by Dr. Anne F. Pierce conducted a study of voles to investigate the effects of “love” on brain chemistry. Their research provides insight into the relationship between romantic partners, social behavior, and dopamine, a brain chemical that makes you feel satisfaction and pleasure. They also investigated how periods of separation affected these social behaviors and dopamine release. Prairie voles were used to study these because of their monogamous and lifelong partnerships. The formation of these bonds are facilitated by mating, which triggers a release of dopamine and results in observable social preference for mates.
The Potential Future of Cancer TreatmentVarun Chafekar, March 31 2024
Proteins are an essential part of the body as they carry out most functions, such as metabolism and anabolism. However, like any machinery, they have to be dismantled and remade to ensure functionality and efficiency. This is where protein degraders come in. Humans use the ubiquitin-proteasome system, where proteins are tagged for destruction with tags called ubiquitin and then eaten by the proteasome. Certain protein degraders can harness this system to tag peptides involved in disease development for elimination, such as Proteolysis Targeting Chimera (PROTAC).
Vertical Divider
|
The Potential for Weight Loss Drugs to Reduce InflammationMeli Renteria, March 31 2024
Inflammation is the body’s natural response against injury and infection, protecting against harmful events triggered by toxins, or injury. In acute situations, like cuts or infections, inflammation helps to heal and protect the body. However, chronic inflammation, which persists for several months or years, can be harmful and is linked to various health problems like heart disease, diabetes, and cancer. A recent finding has shown that glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists (GLP-1RAs), can also reduce inflammation.
New Vaccine Based on DNA Scaffolding Improves ImmunityEmeline Wagner, March 31 2024
Vaccines are a method of training the immune system to recognize a disease by introducing it to an agent similar to the method of infection, but without the ability to harm the body. Many Americans are already familiar with this concept, especially given the recent vaccine protecting against Covid-19, a disease caused by the SARS-CoV-2 virus. One particularly effective form of vaccine is a particulate vaccine, which utilizes a protein scaffold called protein-based virus-like particles (P-VLP) mimicking the virus to deliver antigens or copies of the virus to B-cells: white blood cells that produce antibodies that fight against infection.
PTSD: Separating Sadness from TraumaLuke Porciuncula Gonzales, March 31 2024
Post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) is defined as a disorder where recall of traumatic events leads to negative stimuli with significant effects on an individual’s well-being (American Psychiatric Association). Prior PTSD research has focused on the neural mechanisms underlying non personal memory; however, the correlation between traumatic and nontraumatic memories still remains unclear. In order to better understand this distinction, researchers from the Icahn School of Medicine designed a study to compare and contrast responses to traumatic and nontraumatic memories.
|
New Alzheimer’s Drug Sees Success, FDA ApprovalBlake Schultz, December 29 2023
With the median age of Americans increasing, certain neurodegenerative diseases may be on the horizon for the aging population. Affecting an estimated 6.7 million Americans aged 65 and older, Alzheimer’s disease is a progressive neurological disorder that results in memory and cognitive decline. It is often characterized by confusion, forgetfulness and/or inability to perform daily functions. Despite the high prevalence (roughly one in ten seniors) and extreme effects on the most vulnerable members of the population, there is no cure for Alzheimer’s.
Vertical Divider
|
Low Ovarian Reserve: Does this Impact the Ability to Give Birth?Autumn Jackson, December 29 2023
Many women have low ovarian reserve, which can affect their ability to have children. Generally, women are born with a set number of eggs and gradually lose these eggs as they grow older. Low ovarian reserve causes a woman to have fewer eggs than normal for her age, which may result in her having trouble having children without medical assistance. If a woman is experiencing infertility, doctors can perform tests to diagnose low ovarian reserve.
|
New Insights in the Potential of Liposome-CRISPR TechnologyMeli Renteria, December 29 2023
You may have heard the excitement around CRISPR in the science world and may be wondering— what is it? ‘CRISPR’ stands for Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats. It is a genome editing tool that allows precise changes to DNA sequences, therefore correcting mutations and potentially treating various diseases. CRISPR/Cas9 technology is made up of two components: a Cas9 nuclease, functioning like molecular scissors that cleave DNA strands, and a guide RNA (gRNA), a series of nucleotides serving as a roadmap directing Cas9 where to cut.
Vertical Divider
|
Trigger Warnings: Not As Helpful as You ThinkCrystal Hsueh, December 29 2023
Trigger warnings are alerts about content within a piece of text or media that may contain sensitive topics and themes related to the reader’s past negative experiences. The use of trigger warnings, also known as content warnings, has been increasingly encouraged throughout social media and online news sites. Advocates of trigger warnings argue that warnings help readers emotionally prepare for or have the opportunity to avoid distressing material, claiming that they are a necessary form of disability accommodation.
|
The Effects of Physical Education on Academic PerformanceLuke Gonzales, December 29 2023
Physical education (PE) has become a staple in modern education due to its positive impact on the physical fitness of growing students. While many venerate PE for this attribute, few studies have been conducted on the effects of PE class on a student’s academic performance in other subjects. One recent study was conducted on this basis to investigate the effects of PE during different times of the school day.
Vertical Divider
|
Medical Student Well-being: Insights and SolutionsSatvik Saripalli, December 29 2023
A recent study from Nature analyzed medical student’s well-being to determine causes of distress and possible solutions. Medical students often experience stress, burnout, and other indicators of distress which negatively affects their health. Researchers have linked these indicators to many factors such as low test scores and mistreatment from faculty. However, there are proposed solutions such as implementing pass/no-pass classes, increasing social interaction, and reducing unnecessary information in courses.
|
Babies and their Super Immune ResponseEleanor Gorham, December 29 2023
Babies are known for a lot of things. One of them is being snotty, a trait sometimes found displeasing and unendearing. However, a new study has shown that this mucus provides a strong level of protection against COVID-19 infection. Compared to adults, infants and young children produce antibodies against COVID-19 that last longer and have an overall faster immune response to the virus. A healthy immune response has multiple parts to it: the innate immune response and the adaptive immune response.
|
Polygenic Testing Produces Poor ResultsAndrew Camacho, December 29 2023
As disease screening becomes a more widely accessible tool for people to assess their health, it is becoming important to understand how reliable these preventative measures can be. A recent study conducted by University College London showed that polygenic testing yielded inaccurate and misleading results when employed in a large population. This study utilized the data published in a Polygenic Score Catalog from April 2022 for a secondary analysis by calculating detection and false positive rates.
Vertical Divider
|
The Benefits and Risks of CaffeineWayne Chiang, December 29 2023
Caffeine is a widely available and consumed compound that is commonly found in coffee, tea, soft drinks, and more. More than 85% of the adult population in the US consume caffeine daily. It is often consumed for its properties as a stimulant, anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and pain management and can be found in multiple over-the-counter medications. Due to caffeine's wide usage and few adverse effects, considerable research has been done on its potential medical benefits.
|
Playing Video Games May Lower Depression SymptomsCrystal Ma, September 16 2023
Depression is a mood disorder that currently affects approximately one in every four American adults a year. Individuals with depression can experience symptoms such as constant feeling of sadness, suicidal thoughts and tendencies; these symptoms are felt at different intensities according to an individual’s level of depression. Subthreshold or mild depression, where individuals show some signs of depression, can quickly turn into major depression, a condition that significantly burdens one’s daily life.
Vertical Divider
|
Forgot to Take Your Pills? This Medication Can Help With That.Kruthica Dama, September 16 2023
Pills, or small capsules with a measured amount of drugs inside, have become one of the most recognizable and common forms of medication. Advances in medicine have allowed patients to live longer with a better quality of health, yet when people don’t take their medicine regularly nor at the proper times, these benefits can be limited.
Vertical Divider
|
Pollution and Influenza Amongst Expecting MothersAndrew Camacho, September 16 2023
Vulnerable populations, such as immunocompromised people, may suffer greatly from air pollution, especially in urban areas. In a recent study, a group of researchers determined that pregnant mothers were more likely to have a more severe reaction to influenza when exposed to ultrafine particles (UFP) in the air. This study was conducted on a group of pregnant mice who were subject to UFP exposure to test if the particles led to an abnormal immune reaction which increases infection severity.
|
Could an Injection be the Answer to Obesity in Children?Sabrina Ghalambor, September 16 2023
Obesity has been a rising issue in the United States over the past few decades. Not only has it affected the health of over 42% of Americans, it has also affected nearly 20% of American children. There have been many initiatives in the past to encourage more activity and healthier eating for children over the last decade, such as First Lady Michelle Obama’s efforts to make school lunches more nutritious, but the problem still looms and poses a threat to the health of children across the US. However, the public conversation surrounding obesity has shifted over the last year due to a new medication that entered the scene: semaglutide.
Vertical Divider
|
Hearing Loss and DementiaMichelle Yeung, September 16 2023
Dementia is a loss of cognitive thinking such as memory, emotions, and reasoning caused by failed nerve cell function. Some forms of dementia include Alzheimer’s disease (AD) and vascular dementia. Contrary to popular belief, dementia is not a part of normal aging. Yet, one in ten Americans age 65 and older have dementia. These people suffer from forgetfulness, difficulty concentrating or learning, mood shifts, and coordination issues. Recently, scientists have been exploring hearing loss as a risk factor for cognitive decline and dementia.
|
A New Approach for Treating EpilepsyOlivia Zhou, September 16 2023
Epilepsy is a brain disorder in which sudden changes in the brain’s electrical activity cause recurrent seizures, which in turn manifest as involuntary changes in movement, sensation, or consciousness. For instance, seizures may range from a few muscle jerks to severe convulsions. While drug, diet, and surgery options exist for treating epilepsy, their use depends on restrictive criteria; for example, the diet treatment is mainly effective in children with a specific type of epilepsy. Similarly, surgery is only considered for specific types of epilepsy and would not result in major complications.
Vertical Divider
|
New Drug for Type 2 Diabetes in the WorksAnnie Liang, September 16 2023
The occurrence of type 2 diabetes in America is no surprise, with more cases emerging within younger children and teens. Individuals with type 2 diabetes have issues with regulating sugar due to insulin resistance, leading to high blood sugar levels. While the disease currently has no cure, there are ways to manage the disease: exercise, maintaining a healthy diet, and other medications. To add on to the current standard of care, a drug called tirzepatide was recently approved for the treatment of type 2 diabetes and works by targeting naturally occurring hormones responsible for controlling blood sugar levels.
|
Intratumoral Microbiome and its Role in CancerOlivia Zhou, April 2 2022
The tumor microenvironment (TME)—or the environment around the tumor consisting of numerous components such as different kinds of cells, blood vessels, or extracellular matrix—plays a significant role in the development of cancer. Complex interactions between the tumor and the TME contribute to cancer progression.
|
Effects of Aerobic Exercise on Parkinson’s Disease SymptomsCrystal Ma, April 2 2022
Parkinson’s disease (PD) is a nervous system disorder that can cause a gradual decline in the ability to perform daily tasks. For instance, PD can cause an individual to experience slowed movements, stiffness, and dementia. This disease has become widespread over the years with 8.5 million individuals being diagnosed with PD as of 2019. Because PD is a condition that has no known causes and manifests later on in an individual’s life, there are currently no ways to prevent the disease.
Vertical Divider
|
REMS Triage Method Breakthrough
Anna Chassion, April 2 2022
In emergency medicine, everything is fast-paced. Responders must make pressured decisions in order to provide the best possibility of a positive outcome for the most patients. These decisions determine how serious a patient’s illness is and what kind of care they will receive, as well as how likely the patients are to die. This decision-making process is called triage and it works by a standardized formula. This formula is then tweaked to better predict patient outcomes.
|
Manipulating Genetics in Mice to Explore ADHD Treatments
Anjali Roy, April 2 2022
Attention Deficit Hyperactive Disorder, or ADHD, is one of the most common neurodivergent conditions diagnosed amongst youth in the United States, and the symptoms can continue well into adulthood. Characterized by lapses in attention, restlessness, and impulsivity, ADHD was diagnosed in about 9.8% of American children ages 3-17 in 2019, and in about 4% of American adults ages 18–44.
Vertical Divider
|
Mono & College Students: Implications of the Latest FindingsCatherine Lirtsman, April 2 2022
The infectious disease mononucleosis, or mono, can affect anyone, yet teenagers and young adults should beware. It is increasingly frequent between the ages of 15–24 because of how strongly the immune system reacts to the virus that causes it, the Epstein-Barr virus (EBV). Common mono symptoms are fatigue, swollen lymph nodes, sore throat, swollen liver and/or spleen, and more. These symptoms can last from two weeks to six months. One of the major complications associated with mono is an enlarged spleen.
|
How Urban Areas Affect Students
Varun Chafekar, April 2 2022
The colleges and universities in major cities are melting pots for students coming from all over the globe. The places these young adults hail from can range from urban areas to rural towns, and, as such, the change in environment can have a large impact on students. Life in urban cities can be difficult to adjust to, and researchers wanted to observe how this type of environment would affect adolescent mental health.
Vertical Divider
|
Concussions and an Early Return to School
Andrew Camacho, April 2 2022
Children are often susceptible to receiving concussions due to falling, contact sports, or other reasons. As a result, they are forced to miss school in order to fully recover. There is little information known on the amount of school absence a concussed child should receive, leaving it entirely up to the family’s discretion. However, a recent study has shown that children with concussions may experience a lower symptom burden (nausea, confusion, headache, dizziness, etc.) and an overall faster recovery by returning to school earlier instead of later.
|
Beneath the Polish: Are Manicures Dangerous?Erin Tabornal, April 2 2022
In recent years, going to the nail salon to get your nails done has become an integral part of many individuals’ self-care regimens. While this hobby is enjoyable and seemingly harmless due to its superficial nature, the technology involved with the process has raised concerns about an increased risk in skin cancer. A recent in-vitro study demonstrated that radiation emitted by ultraviolet nail polish dryers can damage DNA and lead to mutations.
Vertical Divider
|
The Father's Brain during the Transition to ParenthoodJenna Hartstein, December 28 2022
The transition to parenthood can be an exciting time, but also a time filled with many changes in sleep, physical habits, and overall stress. Because of the importance of this period, becoming a parent has been deemed a critical window for determining future health outcomes for parents. Much of the existing research focuses solely on the mother during this critical window. However, evaluating the role of fathers provides an interesting perspective as they do not directly experience pregnancy, and are generally understudied. This will allow public health officials to enact better guidelines to best support fathers during this transition.
|
A New Way to Detect an Undetectable DiseaseAnnie Liang, April 2 2022
Alzheimer’s disease is a neurodegenerative disorder where the neurons in the brain gradually stop working. It results in commonly known symptoms: memory loss, difficulty thinking, and much more. The disease is usually in the form of late-onset Alzheimer's. This means there aren't any symptoms for the first 15–20 years, but the symptoms manifest after the age of 65. Due to the delayed onset, it is often difficult to detect the disease. However, With the recent discovery of a potential early marker for Alzheimer's, it may be possible to detect the disease up to 17 years before symptoms begin showing up.
Vertical Divider
|
Eating Late at Night Could be a Risk Factor For ObesityYuki Duong , December 28 2022
Obesity is associated with high blood pressure, increased blood sugar, and a higher risk for heart disease and type II diabetes. But it’s not a disease with a simple cause. So many factors can influence weight gain, such as genetics, diet, and environment. For example, according to a recent research study from Northwestern University, one of the possible risk factors for obesity is the time you eat. Specifically, their study suggests that late-night snacking could lead to weight gain.
|
Psychedelic Drugs as Inspiration for Safer AntidepressantsAnjali Roy, December 28 2022
Depression is one of the most common mental health illnesses in America. It is characterized by feelings of low self-esteem, unhealthy alterations in sleep or eating patterns, fatigue, difficulty concentrating, etc. According to the National Institute of Mental Health, approximately 8.4% of the U.S. population experienced at least one major depressive episode in 2020. Current treatment plans include talk-based therapy or prescribed antidepressants, such as serotonin-reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), which function by increasing serotonin levels in the brain—a hormone that positively regulates emotions.
Vertical Divider
|
Signaling the Immune System to Eat Tumor CellsOlivia Zhou, December 28 2022
Neuroblastoma is a cancer of immature nerve cells, and most commonly affects infants and children. In general, it has one of the lowest survival rates for pediatric cancers, as the five-year survival rate is 50% for high-risk neuroblastoma patients. Furthermore, 60% of the high-risk group will relapse, and their five-year survival rate drops down to less than 5%. Current treatments include chemotherapy combined with anti-GD2 antibodies that target GD2, a molecule overexpressed (present at high levels) in neuroblastoma. Antibodies can target molecules and block them from binding to whatever they normally bind to, thus inhibit their normal effect.
|
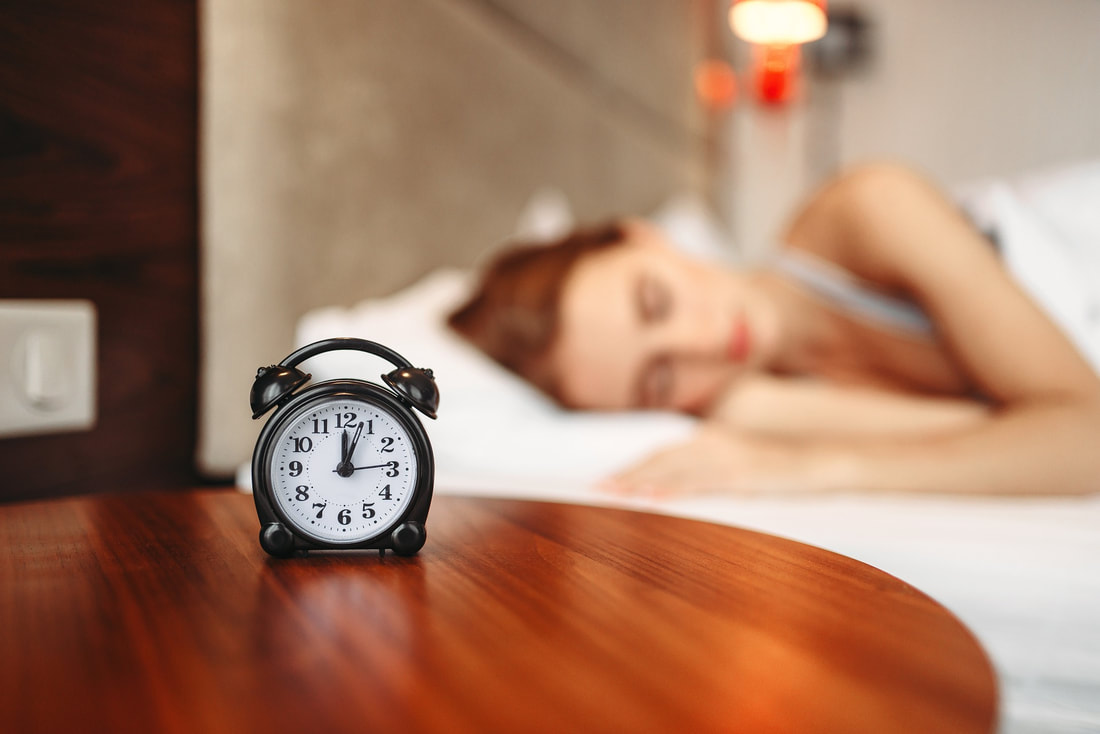
How Much Sleep is Best?Varun Chefkar, December 28 2022
Sleep is one of the most important needs of the human body. To stay healthy, good sleeping habits are a must. However, how much sleep should the average person be getting per day, and how exactly does the amount of sleep one gets affect the body? A research group decided to tackle these questions. The study shows that a lack of sleep is much more detrimental to the body than just feeling groggy when waking up early. It physically affects the brain, an essential organ for most actions.
Vertical Divider
|
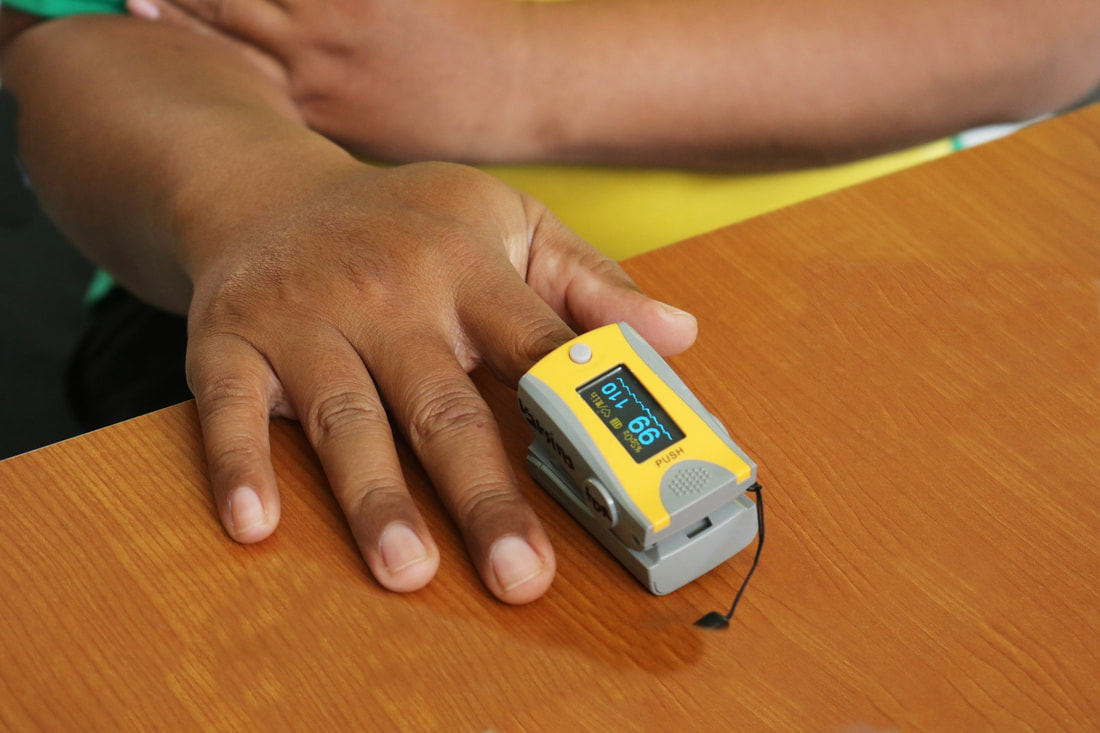
How a Tiny Machine Creates Inequality in HealthcareKruthica Dama , December 28 2022
Hemoglobin proteins work as tiny delivery trucks in the bloodstream to make sure that oxygen is delivered from the respiratory system to the rest of the body. If hemoglobin proteins don’t carry enough oxygen in the blood, a state known as hypoxemia, the rest of the body may not work properly. To easily check blood oxygen levels at home without drawing blood, a device called a pulse oximeter was created. Pulse oximeters use lasers to estimate oxygen saturation, the amount of oxygen carried by hemoglobin. Because they use light as a sensor, changes to surface color, such as adding nail polish or having a darker skin color, affect the way that they read the oxygen values.
|
The Potential Effects of Light Exposure at NightMichael Lee, December 28 2022
In the growing digital age, it’s hard to go about our day normally without being exposed to the light constantly emitted from the screens all around us. Exposure to light, including the light that comes from our everyday phones or computers, greatly affects the body’s circadian rhythm, or “biological clock.” Essentially, the circadian rhythm’s job is to regulate how we act and behave depending on the time of day. For example, it tells us when we want to go to sleep in response to the darkness of night, and also helps us wake up in response to the morning light.
Vertical Divider
|
Early Bird Gets the Worm...But not Diabetes or Heart Disease?Erin Tabornal, December 28 2022
For centuries, the phrases “early bird” and “night owl” have often been used to describe an individual’s preferred duration of wakefulness and productivity. It is a common recommendation that the average human adult should get about seven to nine hours of sleep each day in order to function their best, regardless of when they wake up. However, a recent study from researchers at Rutgers University highlights that early risers may have a lower risk of diabetes and heart disease than late risers.
|
Social Camouflaging and its Impacts on Autistic AdultsWayne Chiang, December 28 2022
Autism spectrum disorder, also known as ASD, is a condition that changes how a person interacts with other people and their environment. This includes struggling in several social situations, from being unable to distinguish social cues to having difficulty communicating with others. Under such circumstances, individuals diagnosed with autism face immense societal pressure to try and seem “normal” through social camouflaging. Social camouflaging is the deliberate act of suppressing characteristics associated with autism in social settings.
Vertical Divider
|
Hair Straighteners and Uterine CancerAndrew Camacho, December 28 2022
Although hair straighteners seem harmless and are often used for cosmetic purposes, recent findings have revealed a possible risk associated with their use. Researchers found a connection between using hair straighteners and the occurrence of uterine cancer. This eleven-year study consisted of 33,437 women ranging from ages 35–74. Participants were initially evaluated using a questionnaire that asked if the women had used hair products such as hair dye, straighteners, relaxers, pressing products, and perms. Other factors such as race, ethnicity, weight, physical activity, and alcohol consumption were taken into account with the questionnaire.
|
Physical Exercise Aids Treatment of Depression and AnxietyCrystal Ma, December 28 2022
Depression and anxiety are common disorders today with depression affecting 17% and anxiety disorders affecting 31.9% of adolescents in the United States. Adolescents with depression are also extremely likely to have anxiety, with three-quarters of children experiencing both. These mental health illnesses affect the lives of adolescents drastically, causing negative interferences with their education, as well as their daily life and function.
Vertical Divider
|
Artificial Human Microbiome and Research in Gut HealthJuliette Williamson, December 28 2022
As the interconnected relationship between the human gut microbiome and both physical and mental well-being becomes increasingly apparent in recent studies, the limitations of currently available research methods have become glaringly obvious. In order to address this issue, a team of researchers led by Dr. Alice Cheng, a Stanford University gastroenterologist, a specialist in treating illnesses relating to our gastrointestinal tract, has built the very first complex synthetic microbiome.
|
Specifically Targeted Cancer Therapy Activated by LightAnnie Liang, December 28 2022
As cancer becomes more common, cancer research has become the forefront of biological and chemical research. A new study that has been published within the last few months has found success in using a cancer-killing molecule activated by light to destroy cancer cells that would otherwise be resistant to chemotherapy. Chemotherapy is a drug treatment used to kill cells that are growing rapidly, which is why it is sometimes able to target rapidly growing cancer cells to treat cancer. This treatment is often given into a vein through a needle, whereby the drugs flow throughout your body to kill cancer cells—especially cells that are rapidly dividing. However, this cancer treatment doesn’t always work when cancer cells change or have properties that do not allow for the drug to interact with the cell, thus rendering the treatment ineffective.
Vertical Divider
|
Saving the Brain After a StrokeArthur Huang, September 26 2022
With one person dying from stroke every 3.5 minutes in the United States, strokes are one of the leading causes of death. Approximately 87% of strokes are ischemic strokes, which are due to a blood clot blocking a blood vessel that supplies parts of the brain, preventing cells from receiving the oxygen and nutrients that they need. In an ischemic stroke, the damaged brain region is composed of an ischemic core, where there is a dramatic decrease in blood flow, and the ischemic penumbra, a region surrounding the core that is at risk of damage but still salvageable and fully functional if properly treated. Based on previous research, one of the main roadblocks in rescuing the penumbra is excitotoxic cell death, resulting from the neuronal release of an excessive amount of the neurotransmitter glutamate. A recent study from Johannes Gutenberg University Mainz sought to find a new therapeutic method for saving the penumbra.
|
Could Light in Your Bedroom Impact Your Metabolism?Diviya Khullar, September 26 2022
Many people underestimate the importance of a good night’s sleep. While a good night’s sleep is known to have a significant impact on one’s mood and energy, studies have shown that it also greatly improves one’s metabolism. Exposure to artificial light has been linked to decreased quality of sleep and even obesity. There has been a lot of interest in studying the effect of ambient light during sleep on metabolic function, and there have been a few proposed explanations as to why they are so closely linked. One explanation is that since light inherently impact’s the duration and quality of one’s sleep, this disturbance results in decreased metabolic function. Another theory is that metabolism is linked to one’s circadian rhythm, the body’s internal clock that times essential processes.
Vertical Divider
|
Saffron Extract in Improving Sleep QualityCrystal Ma, September 26 2022
Sleep disorders such as insomnia have become an increased health issue in the world, with 50-70 million adults in the US alone suffering from a sleep disorder. In people with insomnia, sleeping pills may be used as a form of treatment, but the user may build up a tolerance to the drug, causing it to be less effective. Due to these issues, there is an ongoing search for a safer, more efficient form of treatment. Research recently published by researchers at the Center of Investigation in Clinical Nutrition of the Université catholique de Louvain suggests that saffron may be beneficial in improving sleep quality and sleep duration
|
Teenage Mutant Ninja Turtles: Alzheimer’s and Your DNAEleanor Gorham, September 26 2022
Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is a condition that afflicts millions of people around the world, involving progressively worsening memory loss. Alzheimer’s also affects aspects of thought and language, although the specific mechanisms can be complicated and mysterious. As AD progresses, neurodegeneration, or the slow decline of function in the brain, also progresses. However, the relationship between these two events is still unknown. A recent study examined the relationship between these two biological events by looking at the DNA genome of individual cells. Through investigating the DNA of a single cell, researchers were able to find patterns in DNA mutations in relation to neurodegeneration.
Vertical Divider
|
Trapping Sperm in Gel Could Lead to New Male ContraceptiveAnjali Roy, September 26 2022
Contraceptives refer to methods or medical devices used to prevent pregnancy and allow for safer, healthier intercourse. Effective contraceptive methods play a significant role in decreasing pregnancy-related morbidity and mortality rates and preventing the transmission of sexually transmitted diseases. Current forms of medical contraception, however, are typically targeted towards females, such as birth control pills—hormonal medications designed to stop ovulation (the release of an egg)—or intrauterine devices (IUDs)—technology inserted into the uterus to prevent sperm from traveling effectively. However, besides condoms or spermicides, there are not as many options available for men.
|
Impact of COVID-19 Virus on Kidney CellsAnnie Liang, September 26 2022
With surges in SARS-CoV-2 virus infection globally, it is important to understand the long-term implications that this virus may have on one’s health. During the pandemic, there has been a surge in reports of patients experiencing acute kidney injury in severe COVID-19 cases. This was not only limited to patients with a past history of kidney complications; even infected patients who had never experienced kidney-related issues were developing kidney disease. As such, a recent study conducted by Duke researchers sought to further investigate this by better understanding how the virus can affect human kidney cells.
Vertical Divider
|
Maintaining or Discontinuing Antidepressants in Primary CareIra Kadet, September 26 2022
Depression is a common mental disorder that causes a person to experience a depressed mood, loss of interest and pleasure, and feelings of helplessness that can persist for very long periods of time. Strikingly, depression among adults in the United States has nearly tripled since the COVID-19 pandemic started in 2020 and rates of depression continue to remain at the same elevated level. Of the many avenues for treating depression, the prescription of antidepressants is one of the most prevailing methods used today due to its accessibility and mainstream acceptance. An abundance of research is being performed on the consequences of using and discontinuing antidepressants. One study in particular examined the effects of coming off antidepressants during the maintenance phase of treatment.
|
Mutations Across the Animal Kingdom: Secrets of Human AgingZoe Staggs, September 26 2022
Evidence suggests that the accumulation of molecular and cellular damage, such as somatic mutations, ultimately determine lifespan beyond age 65. Environmental stressors such as air pollution, ultraviolet light, and alcohol consumption can be potent enough to directly damage tissues and cells; with enough cell damage, carefully-regulated processes can be altered and cause uncontrolled cellular division known as cancer. By this logic, it should follow that the more cells there are in the body, the more opportunities there are for cancerous mutations to arise in the body. However, insight into the animal kingdom tells a very different story.
Vertical Divider
|
Could Your Poop Help Solve Psychiatric Problems?Sabrina Ghalambor, September 26 2022
In recent years, scientists have begun researching the possibility of improving gut health using fecal microbiota transplants (FMT). This process requires implanting the feces of a person with a healthy digestive tract into a recipient. The purpose of this transfer is usually to restore crucial bacteria to the gut after a course of antibiotics, which are drugs used to treat certain bacterial infections and can be taken for a variety of illnesses. Antibiotics kill the harmful bacteria causing illnesses, but the process of taking an antibiotic course can also kill beneficial bacteria in the gut; FMT can help restore these bacteria, and has also been used to treat Clostridium difficile and irritable bowel syndrome (IBS). However, the procedure is still a highly experimental procedure, meaning that it has not been studied extensively and needs more testing before it can become a widely available treatment.
|
Can Radiation Therapy Boost the Immune System's Fight Against Cancer?Olivia Zhou, September 26 2022
Radiation therapy is a potent cancer treatment that involves firing high doses of radiation to kill tumor cells or hinder their growth. This therapy is successful because it utilizes ionizing radiation, which has enough energy to damage the DNA present in cells. However, there is DNA in all cells, whether it’s a cancerous or healthy cell; thus, radiation doses may also indiscriminately affect healthy tissue, resulting in toxic side effects. Therefore, it is important to investigate the impact of radiation therapy on healthy tissue in order to evaluate the success and effectiveness of the treatment. In a study in the Journal of General Physiology, Tandl et. al. investigated how X-ray radiation affects the properties of T cells, one of the major components of the adaptive immune system that specifically target pathogens, infected cells, or cancerous cells for elimination.
Vertical Divider
|
Identifying the Biological Basis of AutismMarissa Pennino, September 26 2022
The biological basis of autism — a developmental disorder that poses challenges to an individual’s ability to communicate and interact — has long been disputed amongst medical professionals. This misunderstanding was particularly sensationalized following the release of Dr. Andrew Wakefield’s since-retracted 1998 paper, which concluded that childhood vaccinations, such as the measles, mumps, and rubella (MMR) vaccine, could lead to autism. However, researchers have recently made a breakthrough in the quest for finding the cause of autism, finding that cells called astrocytes play a key role in autism spectrum disorder (ASD) development through abnormal calcium signaling in the brain.
Vertical Divider
|
Vitamin D Deficiency and PCOS: Association and RisksMia Kim, September 26 2022
Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome (PCOS) is one of the most common disorders of the endocrine system, affecting between 6% and 12% of people with ovaries. PCOS is often characterized by irregular periods, elevated androgen levels, and/or cysts in the ovaries. Firstly, individuals affected by PCOS often have irregular periods, or menstruation cycles that are abnormally heavy, long, or infrequent. Individuals may also show physical signs of excess androgen, such as hirsutism (excess facial and body hair), severe acne, or androgenic alopecia (male-pattern baldness).
|
Effects of OTC Teeth-Whitening ProductsErin Tabornal, April 25 2022
Americans spend $1.4 billion to purchase non-prescription, at-home teeth whitening kits each year. Because of the desire for pearly white teeth, there is a strong demand for convenient at-home whitening treatments. It is important to evaluate the effects of these products, considering that two common complaints following tooth-whitening treatments are gum irritation and overall sensitivity of the oral cavity. Recently, faculty at the University College London Eastman Dental Institute conducted an in-vitro study that aimed to evaluate the health of dental cells using carbamide peroxide (CP) teeth-whitening treatments.
Vertical Divider
|
A Potential Vaccine for Allergic AsthmaArthur Huang, April 25 2022
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), approximately 8% of adults and 7% of children suffer from some form of asthma in the United States. Treatments typically involve prescribed inhalers, which can administer a variety of drugs—such as corticosteroids that reduce inflammation—to combat symptoms. However, up to 70% of people with asthma are diagnosed with severe asthma. Also known as type 2 asthma, severe asthma is difficult to treat with high-dosage inhaler medication and often requires oral corticosteroids to control it. Researchers from Sorbonne University in France have developed a vaccine that targets IL-4 and IL-13 to treat asthma marked by type 2 inflammation.
|
Cataract Treatment Could Help Prevent DementiaAudrey Banzali-Marks, April 25 2022
At the front of the human eye, there is a lens that light passes through before being processed by the brain. Normally, this lens is clear. Sometimes, however, the lens becomes cloudy, like looking through a foggy window. This is a cataract, a condition common in older adults. Cataracts typically develop slowly, but without treatment, they can fully obstruct vision to the point of blindness. Currently, over 35 million people in the world have some form of cataracts. Of those 35 million, an estimated 20 million are blind because of cataracts. Thankfully, vision can be regained through cataract surgery. According to a recent research study, the benefits of cataract surgery may even stretch beyond correcting blindness.
|
Using Stem Cells to Treat Type 1 DiabetesDiviya Khullar, April 25 2022
Type 1 diabetes (T1D) is a disease in which the pancreas is not able to produce sufficient amounts of insulin, an important hormone. T1D is usually caused by an issue with the islet beta cells in the pancreas that produce insulin. Typically, diabetics take insulin shots to help manage their blood glucose levels, which although effective, is neither very convenient nor a cure for the disease. That is why other options, such as stem cells, have the potential to be more permanent treatments for T1D. Stem cells are a special type of cell that have not developed into a specific type of cell yet. Therefore, they have the potential to be developed into a cell, tissue, or organ that can then be transplanted to make up for the loss of function of damaged cells. In a 2021 trial conducted at the University of British Columbia, patients with T1D received a transplant of stem cells that would become beta cells.
Vertical Divider
|
Redefining the Factors Behind Exercise's Benefits for the BrainMia Kim, April 25 2022
There are many widely-known beneficial effects of exercise on physical health: strengthening muscle, improving blood circulation, and promoting heart health. However, the cerebral (brain-related) benefits of exercise are often ignored. These benefits include slowing both cognitive aging and neurodegeneration. Scientists have previously hypothesized that the cerebral benefits of exercise are possibly due to exercise’s ability to reduce inflammation in the brain or spinal cord, called neuroinflammation, and increase neuroplasticity (the brain’s ability to change and adapt). However, the biological mechanisms through which exercise produces these effects is less well understood. In order to explore these mechanisms, researchers from the Stanford University School of Medicine recently conducted a study.
Vertical Divider
|
New Insights on the Tau Protein in Treating Alzheimer's DiseaseZoe Staggs, April 25 2022
Between 60% and 80% of dementia cases are attributed to Alzheimer’s disease (AD), a neurological condition that progressively destroys memory, cognition, and eventually the ability to carry out everyday tasks. Currently, there is no monotherapeutic cure for the condition, and the number of adults over 65 (the group most at risk for AD) is expected to double within the next 40 years, calling for more effective, accessible, and affordable treatment. A novel study from the University of California, Riverside (UCR) pinpointed the key difference in brain composition between people who developed Alzheimer’s and those who didn’t. Researchers studied different forms of a protein called tau, found abundantly in neurons in the brain.
|
Intervention Programs in Early Childhood May Prevent Future Obesity DietCrystal Ma, April 25 2022
Childhood obesity is a health issue that has become very prevalent: in the United States, 20.8% of children aged 14 are obese, while 17% are overweight. An increase in body mass index (BMI), a value used to determine obesity, often begins when a child is around four or five years old. Children at the ages of four or five who are overweight are much more likely to be obese later on in life, suggesting that the prevention of obesity should begin early on with the implementation of intervention programs in school. Research recently published by Spanish researchers indicates that implementing intervention programs may lead to an overall decrease in children’s BMI, and therefore assist in the prevention of being either overweight or obese.
Vertical Divider
|
The Impact of Varying Exercise Intensity on Children with ADHDJenna Hartstein, April 25 2022
Attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) is the most common neurodevelopmental disorder in children, affecting an estimated 9.4% of American children. Children with ADHD may have difficulty focusing and paying attention, act without thinking of the result, or be overly active. However, ADHD can be managed, and research continues to be conducted on the most effective treatments. While medication is extremely effective for many children, some experience unfavorable side effects such as a loss of appetite or problems sleeping. Because of these factors, it is important to evaluate alternative treatments for ADHD, such as exercise. One recent study attempted to determine which exercise conditions improve mental health the most in children with ADHD.
|
Potential Long-Term Impacts of Early-Life Western DietAnnie Liang, April 25 2022
Children are often taught to eat healthy food to maintain good health, development, and growth. However, the poor diet and lifestyles that have become common in America are persisting despite the known health risks: obesity, cardiovascular disease, and diabetes, to name a few. A new study conducted at the University of California, Riverside provides evidence that further highlights the importance of a balanced diet, especially during one’s childhood. The researchers fed juvenile mice a diet filled with fat and sugar and found that there were long-term impacts on their microbiome as mature mice—even despite the mice switching to a healthy diet when they were older.
Vertical Divider
|
Medical Cannabis: Heightened Withdrawal SymptomsAngelina Yuan, April 25 2022
Both medical and recreational use of cannabis, or marijuana, have seen an increase in popularity due to the legalization of medical marijuanna in multiple US states. However, although doctors have been prescribing medical cannabis to patients, some of the effects of using it are not widely known. A study conducted by a group of researchers at the University of Michigan has provided new insights on the withdrawal symptoms of medical cannabis being used for pain control. The researchers recruited participants reporting chronic or severe pain from three Michigan medical cannabis clinic waiting rooms, resulting in 527 final participants.
|
A Golden Ticket to Treating Antibiotic ResistanceZoe Staggs, January 18 2022
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), around 47 million people in the United States are prescribed antibiotics for infections that don’t need to be treated with antibiotics every year. This overuse has allowed bacteria, viruses, fungi, and parasites to evolve over time, developing the ability to counteract the drugs designed to kill them. As a result, antibiotic resistance has become a burgeoning public health concern worldwide. In the United States alone, at least 2.8 million people acquire antibiotic-resistant infections annually, resulting in over 35,000 deaths each year. A novel study by a joint team of researchers from the University of Leeds, Southern University of Science and Technology, and Fudan University utilizes nanotechnology, specifically gold nanoclusters, to target resistant bacteria.
Vertical Divider
|
New Drug Delivery System: Alternative to Opioid Painkillers?Arthur Huang, January 18 2022
According to the National Institute on Drug Abuse, between 8% to 12% of people using an opioid pain reliever develop some form of opioid addiction. Opioid painkillers are drugs that reduce pain and provide relief while the patient remains conscious. Doctors typically prescribe opioid painkillers to patients to help them manage chronic pain. Unfortunately, the addictive properties of opioids have led to drug abuse and overdose among patients. As a result, researchers have started turning towards local anesthetics that target a specific region of the body as an alternative for chronic pain relief. Site-1 sodium channel blockers (S1SCBs), which include toxins derived from pufferfish and toxic algae, are one class of compounds with local anesthetic properties. A group of researchers from Harvard Medical School explored whether S1SCBs could be safely delivered to a localized area of the body for an extended period.
|
An Optimal Amount of Sleep May Reduce Risk of Alzheimer'sSabrina Ghalambor, January 18 2022
Alzheimer’s disease currently affects over 6 million people in the United States. The disease is associated with the progressive degeneration of connections between neurons in the brain, which weakens cognition, often leading to cognitive decline. Previous research has suggested that there are links between Alzheimer’s and a lack of good quality sleep as well as other sleep disturbances. Another study determined that both a lack of sleep or an excess amount of sleep can contribute to cognitive decline. Recently, neurologists at the Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis decided to study how biomarkers in a person’s DNA combined with poor quality and too much or not enough sleep can increase the risk of developing Alzheimer’s.
Vertical Divider
|
Congenital Heart Disease: Potential Causes and DisparitiesMelody Zaki, January 18 2022
Congenital heart defects (CHDs) include a variety of birth defects that affect the structure and function of a baby’s heart. These defects may affect blood flow through the heart and throughout the rest of the body. The severity of CHDs can range from mild to very severe cases that require immediate intervention. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), about one in four babies born with a heart defect have a critical CHD that requires surgery or other interventional procedures within the baby’s first year of life. Unfortunately, the causes of CHDs in most babies are still unknown. Recently, a team of researchers in Denmark found an association between maternal metabolic disorders and higher risk of CHDs in offspring.
|
An Emerging New Treatment for Chronic Back PainMahima Kunani, January 18 2022
Chronic back pain affects 16 million adults in the United States, and is one of the most frequent complaints that doctors receive from their patients. In fact, chronic back pain is a leading cause of work-loss days due to disability, and treatment for its symptoms is often ineffective. Researchers at the University of Colorado Boulder conducted a study investigating a new four-week psychological treatment for chronic back pain. Evidence from the study supports the idea that a non-drug treatment can provide effective and long-standing relief from chronic back pain. The study found that two-thirds of chronic back pain patients who underwent pain reprocessing therapy (PRT), a four-week psychological treatment, were either pain-free or nearly pain-free after the treatment. Through follow-up appointments, researchers concluded that the relief felt by patients continued for one whole year after PRT.
Vertical Divider
|
New Auditory Device Grants Hard of Hearing HopeAnjali Roy, January 18 2022
As one of the five senses, hearing is an essential ability that many take for granted. However, according to the National Institutes of Health (NIH), about one in eight people ages 12 and up in the United States have suffered from some form of hearing loss in both ears. Those affected by the most common type of hearing loss, sensorineural hearing loss (SNHL), have damaged stereocilia or damaged nerve pathways. This can be caused by a variety of different circumstances, including physical deterioration over time due to aging, illnesses, deafness since birth, etc. There are currently no cures for SNHL. But recently, researchers have sought to create a cochlear implant device that would mimic the function of normal stereocilia in humans and interpret sound.
|
Exciting CRISPR-based Sickle Cell Disease TreatmentNeel Sharma, January 18 2022
In our bodies, the instructions from thousands of genes are necessary for accomplishing essential functions. Even the smallest mutations in our genetic code can disrupt these finely tuned operations, resulting in catastrophic and oftentimes irreparable damage throughout the body. Sickle cell disease (SCD), one of the most common single-gene disorders in the world, results from a point mutation in a gene that codes for a subunit of hemoglobin. This leads to the formation of disfigured red blood cells (RBCs) characteristic of SCD. Considering the large number of people affected by SCD, investigating effective treatment options has been a major priority of the scientific community for quite some time. In a recent article published in the New England Journal of Medicine, results from a clinical trial investigating a new treatment option for SCD indicate promise in identifying a solution for these diseases.
Vertical Divider
|
Reprogramming Neurons to Repair Vision Loss After StrokeDiviya Khullar, January 18 2022
Many people suffer from an ischemic brain injury, a condition where blood flow to the brain is cut off, after a stroke. Depending on where in the brain this occurs, a person could lose a number of important functions, including sight. Once an adult suffers ischemia in the visual cortex, since neurons are not very easily regenerated, they may never be able to see again. However, many studies are looking into methods that could be used to reverse this damage. One approach has been the use of gene therapy to reprogram non-neuronal cells so that they can take on the function of damaged neuronal cells. Researchers from Purdue University have been targeting glial cells, where they are aiming to turn on gene expression patterns that are similar to the neuronal cell in the visual cortex.
|
Robotic Arms: The Next Step in Patient AutonomyAutumn Jackson, January 18 2022
Amputation, the loss of a limb, affects around two million people in the United States. Some of these individuals were born missing all or part of a limb. For others, amputation is the result of traumatic injury, diabetes, peripheral vascular disease, or malignancy. For centuries, humans have been using prostheses, artificial replacements for their limbs. Currently, people mainly use three types of arm prostheses. Patients decide which arm prosthesis best suits them, as all types have their own benefits and drawbacks. As such, researchers conduct studies to test the successes and failures of recent prosthetic technologies to help inform patients’ decisions while also providing insight for the development of new prosthetic models. One study examined the progress of “pattern control systems” in myoelectric arm prostheses.
Vertical Divider
|
The Influence of Baby Formula on Future Disease PreventionCrystal Ma, January 18 2022
Cow’s milk allergy (CMA) is one of the most common allergies in children, affecting about 7% of babies under the age of one. Over the past 20 years, there has been a significant rise in the number of children with CMA. Research also shows that babies with CMA are more likely to develop other atopic diseases, including asthma, eczema, and chronic hives later on. Currently, babies with CMA are to avoid consuming anything containing cow’s milk proteins. As such, those who are not breastfed are fed baby formulas that do not contain cow’s milk proteins. In fact, new findings suggest that ingredients contained in baby formulas may actually help prevent the later development of atopic diseases in children born with CMA. Research recently published by researchers at the University of Naples highlights a five-year-long study that investigated the effects of different baby formulas on children with CMA from infancy.
|