Printable Organs are Closer Than They Appear
3D printers are a relatively new invention that previously had little practical application. For medicine, 3D printing is used for many medical applications with the correct machines and materials. These printers are adept at fabricating tissues and organs and creating prosthetics, which are implants. Overall, this technology has the potential to assist in creating personalized and customized medical products.
While 3D printers have been used to build houses or model buildings, many medical products require materials that cannot be used. The printer manufactures products by depositing input material onto a platform. This technique is an additive manufacturing process. The computer places the material in a pattern that follows a computer design as the model. However, a major limit of the machine is that some items require materials that are not compatible with the inputs of a 3D printer. While the printer can use cells to create tissue, certain advanced products such as thick and complex organs are not able to be manufactured at this time.
Even though complex organs are still out of reach, there are tangible applications of 3D printing that can be seen today. Commercially, it is used to make prototypes as well as fabricating of living tissue in some companies. For consumers additive manufacturing is beneficial because it is a cheap method of printing any materials from medical products to clothes.
For medical practices 3D printing is used mainly for its ability to be customized and personalized through simple changes in the product’s computer code. However, unlike most medical products, Printed products such as prosthetics are much more cost-efficient than traditional prosthetics. 3D printers are also much faster than traditional production techniques. This makes product delivery better and the quality of products is increasing as new technological developments are researched. The code for many medical products is public knowledge, which greatly reduces the cost of products. Also this greatly increases the improvements in code as there are many more researchers that can work on improving the code.
While 3D printers have been used to build houses or model buildings, many medical products require materials that cannot be used. The printer manufactures products by depositing input material onto a platform. This technique is an additive manufacturing process. The computer places the material in a pattern that follows a computer design as the model. However, a major limit of the machine is that some items require materials that are not compatible with the inputs of a 3D printer. While the printer can use cells to create tissue, certain advanced products such as thick and complex organs are not able to be manufactured at this time.
Even though complex organs are still out of reach, there are tangible applications of 3D printing that can be seen today. Commercially, it is used to make prototypes as well as fabricating of living tissue in some companies. For consumers additive manufacturing is beneficial because it is a cheap method of printing any materials from medical products to clothes.
For medical practices 3D printing is used mainly for its ability to be customized and personalized through simple changes in the product’s computer code. However, unlike most medical products, Printed products such as prosthetics are much more cost-efficient than traditional prosthetics. 3D printers are also much faster than traditional production techniques. This makes product delivery better and the quality of products is increasing as new technological developments are researched. The code for many medical products is public knowledge, which greatly reduces the cost of products. Also this greatly increases the improvements in code as there are many more researchers that can work on improving the code.
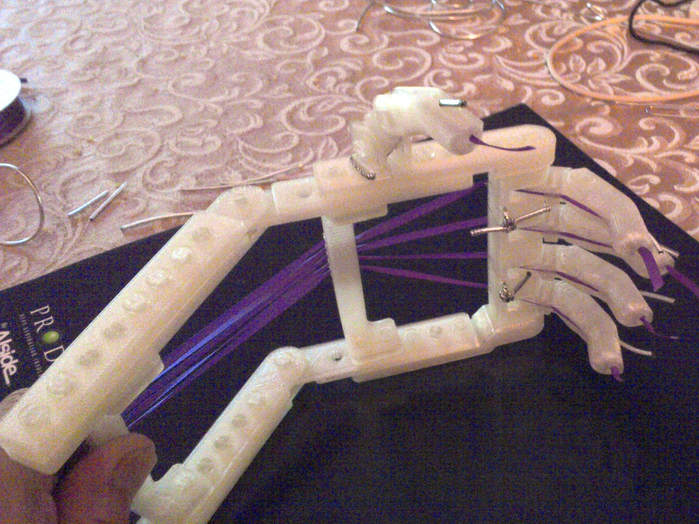
3D printed products can range from bioprinting of live cells, models for surgery, and manufacturing of implants. The human body dies due to individual tissues or organs failing. Instead of receiving transplants from living donors, 3D printing can create tissues and organs available for transplant. This can become an effective replacement for real donors with more research and testing. Rather than making organs, these machines are adept at making limbs. 3D printed prosthetics and implants are used currently used by many people in need of dental, spinal, or hip surgery. It is possible to create new drugs as well. 3D printed drugs are useful because they can combine active ingredients in layers that are usually more expensive. This can help people who need to take multiple types of medicine because the drug can combine the drugs into one pill.
Overall, 3D printing has the ability to be used for medical applications, but as of now the applications are still being researched and developed. This doesn’t mean that 3D printing is useless though. Due to 3D printing’s cost effectiveness speed, and personalization, there is a large push to promote the practice. This could greatly change the face of medicine as the method is used more often and has more practical applications, once there are more technological advances. Nevertheless, to see advancement it is up to consumers and producers to invest in 3D printers.
Overall, 3D printing has the ability to be used for medical applications, but as of now the applications are still being researched and developed. This doesn’t mean that 3D printing is useless though. Due to 3D printing’s cost effectiveness speed, and personalization, there is a large push to promote the practice. This could greatly change the face of medicine as the method is used more often and has more practical applications, once there are more technological advances. Nevertheless, to see advancement it is up to consumers and producers to invest in 3D printers.
RELATED ARTICLES
|
Vertical Divider
|
Vertical Divider
|
Vertical Divider
|