Protein Supplementation and Resistance Training: They Are Not Just for Men
In 2016, the World Health Organization found that 40% of women were classified as overweight and 15% as obese across the globe, with both of these values presented at higher levels than those of their male counterparts. These findings indicate that women may have high percentages of body fat, which can have dangerous health implications including strokes, type two diabetes, and heart attacks.
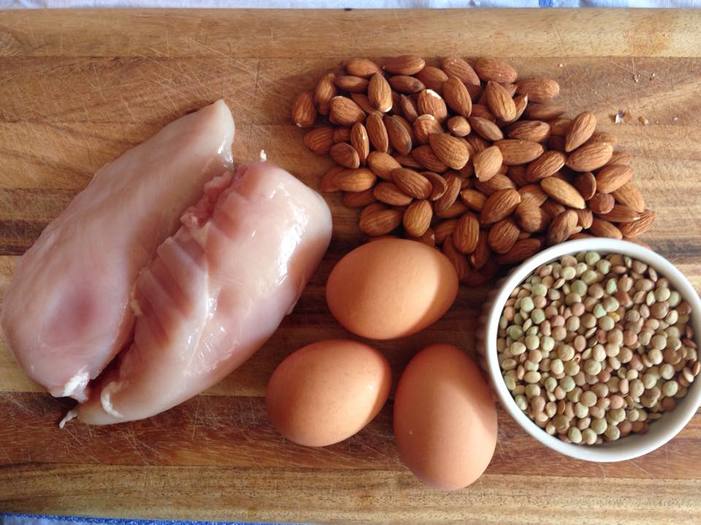
Body fat is one of many factors that comprise one’s body composition, a measure of one’s lean (muscle) mass, bone density, water, and fat in their bodies. In contrast to body fat, lean mass is a beneficial contributor to body composition. Often, it is formed through exercising—particularly resistance training—and eating protein, a macronutrient found in foods such as meat, tofu, and beans. Lean mass increases one’s metabolism, improves bone strength, provides more energy, and lowers the likelihood of developing diseases caused by high body fat percentages.
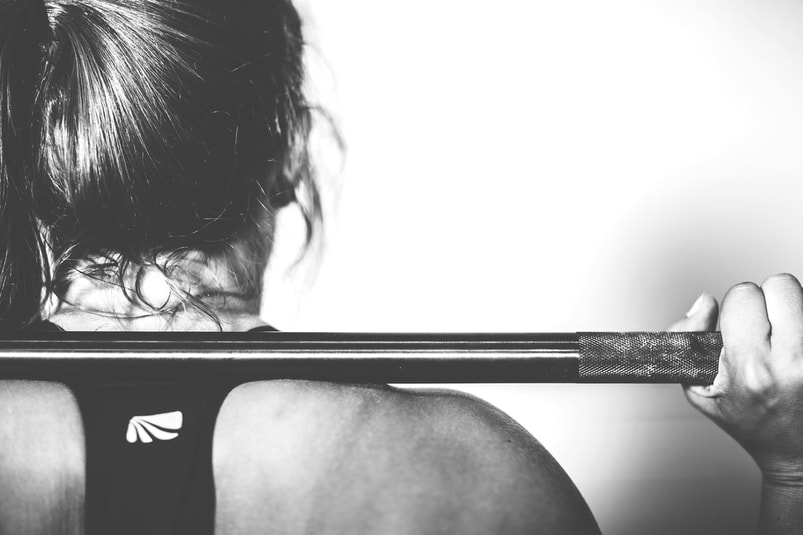
Stereotypically, growing muscle and lean mass is often associated with males, as advertisements for protein supplements and lifting weights have generally been directed towards a male audience. However, studies are finding that not only men, but women too, can improve their body composition through increasing protein in their diets and participating in resistance training, such as lifting weights.
Body fat is one of many factors that comprise one’s body composition, a measure of one’s lean (muscle) mass, bone density, water, and fat in their bodies. In contrast to body fat, lean mass is a beneficial contributor to body composition. Often, it is formed through exercising—particularly resistance training—and eating protein, a macronutrient found in foods such as meat, tofu, and beans. Lean mass increases one’s metabolism, improves bone strength, provides more energy, and lowers the likelihood of developing diseases caused by high body fat percentages.
Stereotypically, growing muscle and lean mass is often associated with males, as advertisements for protein supplements and lifting weights have generally been directed towards a male audience. However, studies are finding that not only men, but women too, can improve their body composition through increasing protein in their diets and participating in resistance training, such as lifting weights.
Image Source: "Protein-rich Foods" by Smastronardo is licensed under CC BY-SA 4.0
A variety of studies measured the effects of resistance training, whey protein supplementation, and a slight caloric deficit on a female’s body composition.
In contrast to subjects without protein supplementation, women who added more protein in their diets tended to have an increase of lean mass with no change in fat mass. Another set of studies pairing increased protein intake with caloric deficit produced even greater changes in body composition in women. Due to the additional protein they were consuming, women were able to reduce their body fat while simultaneously preserving their muscle. Finally, a single study grouping protein supplementation, caloric deficit, and resistance training together showed to have positive effects on body composition. Resistance training is particularly beneficial to improving one’s health by reducing the risk of osteoporosis, stimulating muscle growth, and improving joint and bone strength. Through these studies, it became clear that resistance training, protein supplementation, and a slight caloric deficit assist women in reducing their body fat percentages and increasing lean mass percentages.
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle is possible through a variety of exercise activities and diets, so people should choose a routine which they will be consistent with and enjoy. However, a diet including more protein and a regular resistance training exercise routine will boost one's progress to having a healthier body composition.
In contrast to subjects without protein supplementation, women who added more protein in their diets tended to have an increase of lean mass with no change in fat mass. Another set of studies pairing increased protein intake with caloric deficit produced even greater changes in body composition in women. Due to the additional protein they were consuming, women were able to reduce their body fat while simultaneously preserving their muscle. Finally, a single study grouping protein supplementation, caloric deficit, and resistance training together showed to have positive effects on body composition. Resistance training is particularly beneficial to improving one’s health by reducing the risk of osteoporosis, stimulating muscle growth, and improving joint and bone strength. Through these studies, it became clear that resistance training, protein supplementation, and a slight caloric deficit assist women in reducing their body fat percentages and increasing lean mass percentages.
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle is possible through a variety of exercise activities and diets, so people should choose a routine which they will be consistent with and enjoy. However, a diet including more protein and a regular resistance training exercise routine will boost one's progress to having a healthier body composition.
Featured Image Source: Ichigo121212
RELATED ARTICLES
|
Vertical Divider
|
Vertical Divider
|
Vertical Divider
|