Growth and Containment of Antibiotic Resistant Bacteria
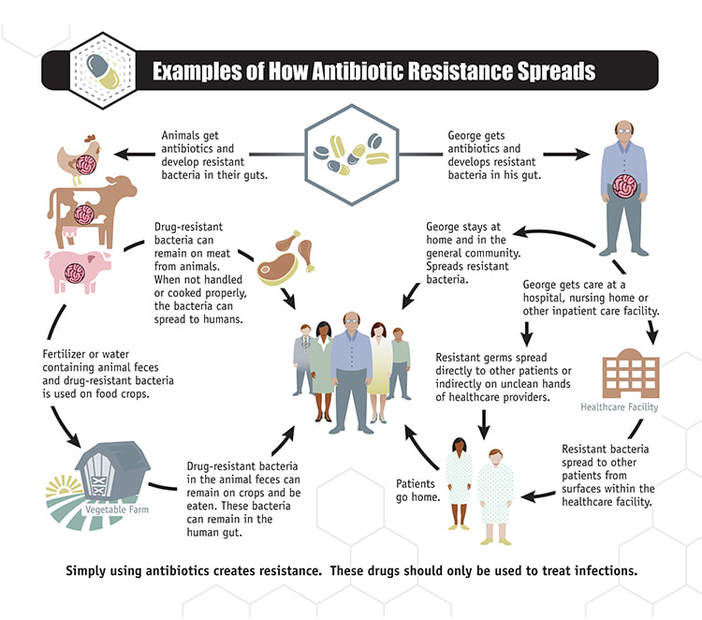
Antibiotic resistance occurs when bacteria become unaffected by drug treatment, allowing the bacteria to grow despite the medication. Resistance can develop from the misuse and overuse of antibiotics, the drugs that are supposed to kill the bacteria. When the antibiotic is given to the patient, it often does its job. However, there may be a few bacteria that, through mutation or by other means, are able to develop resistance to the antibiotics and be unaffected by them. As a result, these pathogens can reproduce rapidly and cause diseases that are difficult to cure. Consequently, this stronger pathogen can spread to other humans and cause an epidemic.
There are not many methods doctors can utilize to treat diseases caused by antibiotic resistant bacteria. Since antibiotics no longer work on the bacteria, all that is left to fight the infection is the patient’s immune system. Sometimes the patient will still be given antibiotics in hopes that it can help fight the infection, but usually it comes down to whether the patient’s body can fight off the infection on its own. Doctors and nurses can also try to relieve the patient’s symptoms and make sure they have enough fluids and nutrients. For example, if the bacteria is a strain of strep throat, doctors and nurses may have the patient rest, drink lots of fluids, and take painkillers in addition to using antibiotics.
There are not many methods doctors can utilize to treat diseases caused by antibiotic resistant bacteria. Since antibiotics no longer work on the bacteria, all that is left to fight the infection is the patient’s immune system. Sometimes the patient will still be given antibiotics in hopes that it can help fight the infection, but usually it comes down to whether the patient’s body can fight off the infection on its own. Doctors and nurses can also try to relieve the patient’s symptoms and make sure they have enough fluids and nutrients. For example, if the bacteria is a strain of strep throat, doctors and nurses may have the patient rest, drink lots of fluids, and take painkillers in addition to using antibiotics.
Image Source: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
It is extremely difficult to control antibiotic resistance because there are currently no methods to control how a bacteria grows and mutates in response to drugs. As a result, immediate response to antibiotic resistance is very important in making sure the antibiotic-resistant pathogen is not spread to more people. The Centers for Disease Control (CDC) highlighted a few steps to respond more efficiently to an antibiotic bacterial outbreak. The first step is to see if there is an outbreak and if the antibiotic bacteria is spreading. Then, it is important to identify which patients are affected by the bacteria. This step includes testing both patients with and without symptoms that may or may not have the bacteria. The final step is to find out if the infection is anywhere else, and this usually includes testing those who live with the patient, such as roommates or family members. In addition, the healthcare facilities where the patient has stayed in the past are screened just in case the infection originated from there. It is also important to make sure healthcare facilities have the resources to follow the guidelines to contain an antibiotic resistant bacteria. After this, those infected are usually tested monthly after the initial outbreak in order to assess if the bacteria needs to be further contained. According to the CDC, facilities that take these precautions within 48 hours of finding antibiotic resistant bacteria stop the spread of the germ.
Antibiotic resistant bacteria is clearly a growing problem, as demonstrated in 2017. There have been 220 cases of antibiotic resistant bacteria. Both methods of prevention by not abusing antibiotics and containing infections quickly are necessary, and both require a change in healthcare culture. Ways to help change how way antibiotics are viewed include using any given antibiotics as prescribed, letting the government know how important it is to have policy that prevents excessive use of antibiotics in livestock, increasing education on the proper use of antibiotics, and not pressuring a doctor to prescribe antibiotics.
Antibiotic resistant bacteria is clearly a growing problem, as demonstrated in 2017. There have been 220 cases of antibiotic resistant bacteria. Both methods of prevention by not abusing antibiotics and containing infections quickly are necessary, and both require a change in healthcare culture. Ways to help change how way antibiotics are viewed include using any given antibiotics as prescribed, letting the government know how important it is to have policy that prevents excessive use of antibiotics in livestock, increasing education on the proper use of antibiotics, and not pressuring a doctor to prescribe antibiotics.
Featured Image Source: qimono
RELATED ARTICLES
|
Vertical Divider
|
Vertical Divider
|
Vertical Divider
|