Climate Change and Its Impacts for Public Health
,Among the many concerns surrounding climate change is the potentially harmful outcome drastic fluctuations in environmental conditions could have on global health. As the severity of climate change continues to exacerbate, human health finds itself in a state of jeopardy due to the issues that arise as a result, such as rising rates of vector-borne disease and food insecurity. The health care systems need to adapt accordingly to the climate change related effects on health, and new policies should reflect the changing behaviors and practices required to combat the degradation of environmental resources. A 2018 report from the Lancet Countdown explores the relationship between health and climate change and claims that our response will influence health outcomes far into the future. The central problem is that the rate at which climate change is worsening is disproportionately greater than the efforts to reverse its effects.
As global temperatures rise, vulnerable populations such as the elderly and those in low-income and middle-income countries (LMICs) are more at risk for disease. The Lancet report detailed increasing trends in non-communicable disease across LMICs and rapidly increasing temperatures in Europe and the eastern Mediterranean. Rapid climate change means rapid changes in food security, water quality, air quality, and spread of diseases. The increased exposure to heat waves across the globe affects food production as it creates difficulties in raising livestock. The report additionally addressed the need for information regarding mental health and climate change as early research indicates that unpredictable extreme weather, heat waves, and natural disasters all contribute to a decreased mental state across populations. These early effects of global warming are indicators of far more severe ramifications to public health, assuming trends of increasing temperature continue in this direction.
As global temperatures rise, vulnerable populations such as the elderly and those in low-income and middle-income countries (LMICs) are more at risk for disease. The Lancet report detailed increasing trends in non-communicable disease across LMICs and rapidly increasing temperatures in Europe and the eastern Mediterranean. Rapid climate change means rapid changes in food security, water quality, air quality, and spread of diseases. The increased exposure to heat waves across the globe affects food production as it creates difficulties in raising livestock. The report additionally addressed the need for information regarding mental health and climate change as early research indicates that unpredictable extreme weather, heat waves, and natural disasters all contribute to a decreased mental state across populations. These early effects of global warming are indicators of far more severe ramifications to public health, assuming trends of increasing temperature continue in this direction.
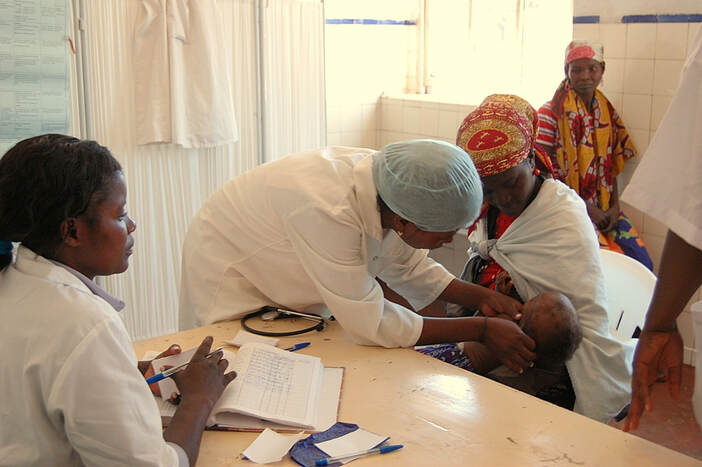
Image Source: "Malaria treatment in Angola" by USAID in Africa is licensed by United States Government Works.
Although there is much cause for alarm, there have been small victories in the struggle against rising global temperatures. The report outlined the many efforts to strive toward sustainability, especially in the energy industry. Since 2013, there has been a steady phasing out of coal and an increased use of renewable energy. These positive trends indicate that it is possible to make advances in public health in the face of worsening environmental conditions; however, the determining factor is the extent to which these mitigating activities occur. Currently, even though the energy industry is making changes in the right direction, the rate at which they are being implemented is not enough to undo the effects of climate change, and any progress may be overshadowed by continually deteriorating global conditions.
Public awareness surrounding the health effects of climate change will influence the global response as informational services enable communities to take action. The report claims that enhanced engagement by the public is imperative for any policy change at the global level. Although attention toward global warming in the media has been increasing, a great deal of coverage overlook its effects as they pertain to public health. There must be a greater level of understanding regarding the intersection between health and climate change to fully comprehend the urgency of the issue. Ultimately, health outcomes for the next several generations rely on current responses to climate change.
Public awareness surrounding the health effects of climate change will influence the global response as informational services enable communities to take action. The report claims that enhanced engagement by the public is imperative for any policy change at the global level. Although attention toward global warming in the media has been increasing, a great deal of coverage overlook its effects as they pertain to public health. There must be a greater level of understanding regarding the intersection between health and climate change to fully comprehend the urgency of the issue. Ultimately, health outcomes for the next several generations rely on current responses to climate change.
Featured Image Source: digifly840
RELATED ARTICLES
|
Vertical Divider
|
Vertical Divider
|
Vertical Divider
|